How to Upload Csv File Into Sas Studio
Equally a Data Annotator, it's common practice to manipulate your data in SAS and consign information technology for further assay. SAS provides many formats to export data, such as CSV (comma-separated values). But, how do yous export your data equally a CSV file?
You lot export SAS data as a CSV file with PROC Export. You provide the Consign procedure with the data you lot desire to consign and the desired location, and SAS will create the CSV file. PROC EXPORT has options to modify the delimiter, print column labels instead of column variables, and remove the header.
Encounter as well – How to Consign Data from SAS to Excel
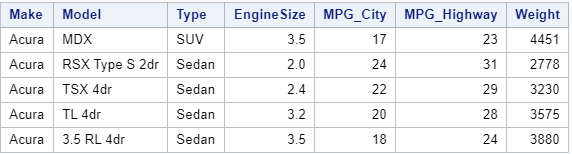
Sample Information
In this article, we use a sample dataset to create a CSV file (work.my_data). This dataset is based on the CARS dataset from the SASHELP library, but with fewer columns.
Do You Know? – How to Select Columns with the KEEP option
Export information from SAS as CSV with PROC EXPORT
The Export Process
The easiest fashion to export data from SAS every bit CSV is with PROC EXPORT. The EXPORT process is a flexible process that can be used to export information in many formats such as Excel (.xlsx), Text (.txt), and Comma Separated Values format (.csv). It also provides options to consign information with unlike delimiters, without a header, or export variable labels instead of variable names.
Syntax of PROC EXPORT
To export data from SAS as a CSV file with PROC Export you need to define at least 3 parameters:
- Data=-option to specify the SAS dataset you desire to export. For example,Information=work.my_data.
- OUTFILE=-option to define the output location and the file name. For instance,OUTFILE="/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv"
- DBMS=-choice to specify the file extension such asDBMS=csv.
DATA=-option
The Information=-option specifies the SAS dataset y'all want to export. You tin either use a one- or two-level SAS name (i.east., with or without libref). When you lot export a dataset as a CSV file, yous can use dataset options such as KEEP, RENAME, and WHERE in the DATA=-option.
OUTFILE=-selection
The OUTFILE=-option specifies the location and file proper noun of the exported dataset. The file name includes the extension. Keep in mind that the complete path (location and file name) can't exceed 201 characters.
DBMS=-pick
The DBMS=-option specifies the type of file the EXPORT procedure creates (e.g., .csv). If you create a .csv file and want to open it with Microsoft Excel, keep in mind the maximum number of rows and columns. Excel can only open files that don't exceed the maximum of ane,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns.
Examples
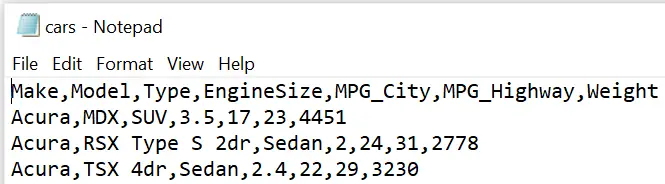
The SAS code below exports thework.my_data dataset every bit a CSV file and creates a file chosencars.csv.
proc export data=work.my_data outfile="/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv" dbms=csv; run; 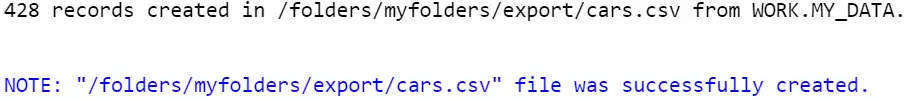
How to Supplant an Existing CSV File
If want to update a previously created CSV file with the Consign procedure, so, past default, SAS won't allow this. The EXPORT procedure protects the existing file and doesn't let you to supersede it. However, you can modify this default behavior. So, how exercise you overwrite an existing CSV file with PROC Export?
You use the REPLACE option to substitute an existing file with PROC EXPORT. The REPLACE option is function of the EXPORT statement and needs to exist placed after the DBMS=-option.
In the example beneath, we replace the cars.csv file.
proc export information=work.my_data outfile="/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv" dbms=csv replace; run; Keep in mind that SAS won't inquire for confirmation to supersede the existing file.
Practise you know? How to Create a Zero File of CSV Files in SAS
How to Change the Delimiter of the CSV File
As the proper noun suggests, the data in CSV files are separated with a comma. Still, for some purposes, it is necessary to modify the default separator (i.e., delimiter). So, how do y'all change to delimiter of SAS' PROC Export?
Yous apply the DELIMITER=-argument to modify the default separator of PROC EXPORT. The DLM=-statement is a synonym of the DELIMITER=-statement and can be used instead. The new delimiter must be placed between quotation marks. Typical delimiters are the semicolon, the forward-slash, or the tab.
The SAS code below we set the delimiter to the semicolon.
proc export information=work.my_data outfile="/folders/myfolders/consign/cars.csv" dbms=csv supervene upon; delimiter=";"; run; 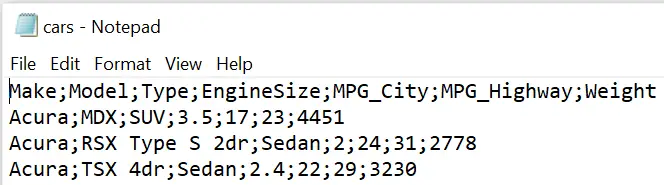
Note: To export SAS data as a tab delimited CSV file you lot take ii options
- Gear up the DELIMITER=-statement to delimiter="09″ten, or
- Prepare the DBMS=-option to dbms=tab and omit the DELIMITER=-statement.
How to Exclude the Header from the CSV File
Usually, you need the header (i.e., cavalcade names) in your output file. That is why SAS includes by default the header in all types of exported files. However, sometimes you lot might need to change this default setting. So, how do you lot exclude the header from the CSV file?
The PUTNAMES=-statement allows you lot to exclude the header from the CSV file. This argument has two options, namely Yep (default) and No. And so, to omit the cavalcade names, you use PUTNAMES=NO.
In the example below, we create a CSV file without header.
proc consign data=work.my_data outfile="/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv" dbms=csv replace; putnames=NO; run; 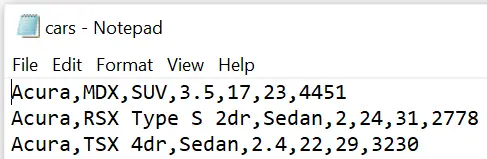
How to Export Variable Labels in a CSV File
SAS datasets take variable names and, optionally, variable labels. Variable labels can comprise special characters such equally blanks and percentage signs. For this reason, variable labels are more than elegant and are often used in reports. Nonetheless,by default, PROC Export exports the variable names instead of the variable labels. So, how do yous export the variable labels with PROC Export?
You utilise the LABEL option to create a CSV file with the variable labels instead of the variable names. You lot place this option later on the Supercede choice. If a variable doesn't have a characterization, then PROC EXPORT exports the variable name.
For case, with the SAS code below we consign the variable labels.
proc export data=work.my_data outfile="/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv" dbms=csv label replace; run; 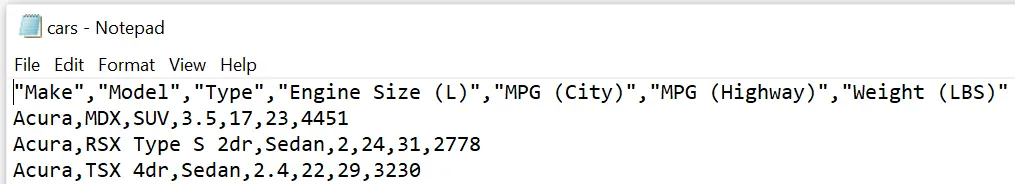
With a PROC CONTENTS statement, y'all can bank check whether a column has a label. For instance, some of the columns of our sample informationwork.my_data have labels.
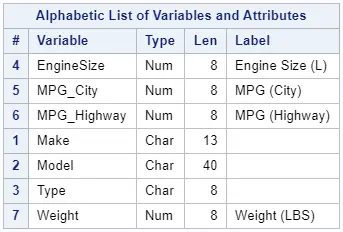
proc contents information=work.my_data; run; How to Change to Encoding to UTF-8
There exist many file encodings. The default encoding is (usually) ANSI. However, you tin can modify the default setting such that you lot tin can export a CSV file a UTF-8.
Yous define the encoding of your CSV file with the global FILENAME statement before the PROC Export. The FILENAME argument starts with the FILENAME keyword, followed by the fileref, the file location (including the filename and extension), and the ENCODING=-option. You use ENCODING="UTF-eight″ to export the CSV file with the UTF-8 encoding.
For example:
filename output "/folders/myfolders/export/cars.csv" encoding="UTF-8"; proc export information=work.my_data outfile=output dbms=csv replace; run; Notation: Instead of defining the location of your file with the OUTFILE=-option, you employ the fileref from the FILENAME statement equally value for the OUTFILE=-option.
Do you know? 3 Ways to Import a CSV File
broussardconevenibary.blogspot.com
Source: https://sasexamplecode.com/how-to-export-sas-data-as-a-csv-file/
0 Response to "How to Upload Csv File Into Sas Studio"
Post a Comment