Does the Baby Start Feeding Off Your Fst if You Dont Eat Enough
Abstruse
Which snack would you adopt? A bag of fries or carrot sticks? Water ice cream or an apple tree? Most of u.s. would probably choose the junk food. While sometimes it is OK to accept fries or ice foam, if you lot eat junk food all the time it is pretty obvious you will brainstorm to gain weight. What might not exist obvious is that a poor diet tin also change your brain! Even before a baby is born, what the parents swallow tin affect how the baby's brain develops. Here, we tested what happens to the brain if nosotros begin to eat healthier as we abound, after eating poorly early on on in life. Nosotros found that eating poorly when the encephalon is developing changes our decisions nearly nutrient. However, we can fix some of this harm with a good nutrition. Excellent news for kids and adults who have health problems from eating a poor diet early in life.
A Baby's Diet Can Change How it Thinks About Food
Scientists now know our nutrition in early life is actually important for our health in the long-term. If your dad was obese when you were conceived, or if your mom ate too much junk food when she was significant with y'all, or if yous started eating fries and drinking cola before you could walk, these bad eating habits tin can play havoc with your encephalon and the mode you retrieve about food. We were interested to see if the negative effects of eating poorly in early life could be reversed past eating a healthier diet as we become older.
How Exercise We Know When We are Hungry?
As both children and adults, we have brains that are usually very good at telling us when we are hungry and when we are full. You may notice that, just before dinner time, y'all start feeling hungry, even if y'all are decorated playing an interesting game. But you do not usually feel hungry all day. This is because we take a hormone called " ghrelin " that increases in the claret just earlier repast times or when we take not eaten for a while.
Ghrelin comes from the stomach and travels in the blood. Ghrelin ends up in the brain and tells the brain to feel hungry and start eating. Just like the players on a football squad, all of the different parts of the brain have different jobs to do. They proceed communicating with each other to assist each other out, just they nevertheless accept adequately separate functions. The part of the brain that ghrelin talks with to tell our bodies that we are hungry is called the hypothalamus . The hypothalamus is really of import. Different parts of the hypothalamus control how stressed we experience, whether we are able to have babies when we abound upward, how thirsty we are, how nosotros grow, and as well…how hungry we feel [1].
Some other of import hormone that tells kids and adults how hungry they experience is leptin . Leptin comes out of the fat in the body and tells us to stop feeling hungry. Leptin is normally present all the time and, like a red traffic calorie-free, it stops us from beingness badly hungry throughout the whole day. But, if we get and then starving that our fat levels decrease, no more leptin is made, and we offset feeling actually hungry once more than. Together, ghrelin and leptin talk to the hypothalamus to make certain that we eat enough to keep our energy levels high and our bodies healthy.
How Does Our Hunger-Sense Develop?
Dorsum to babies, though. Babies that are yet inside their moms do non have to consume to get their free energy. They go their diet and energy from mom. So, when the baby is developing, ghrelin and leptin do a different job. They assist the infant'south brain to develop. Ghrelin and leptin are especially important in unborn babies for making neurons abound between different parts of the hypothalamus [2, 3].
Neurons are tiny cells in the encephalon and they command how dissimilar parts of the encephalon talk to each other and how nosotros become information from our eyes, and ears, and stomachs, to the brain. Most neurons look a bit similar wires with a blob on i end (see Effigy i for a picture show of some real neurons and some diagrams of what neurons expect like). Data is received at the hulk finish, travels downwards the wire (axon), splits, and is delivered to the other neurons at distant parts of the brain.
Fun fact : Most neuron wires (axons) are and then thin that 1,000 of them tin fit in ane mm. The squid has a giant neuron that is so large we tin see it without a microscope. Its axon can be 1 mm broad, the size of a small pencil lead!
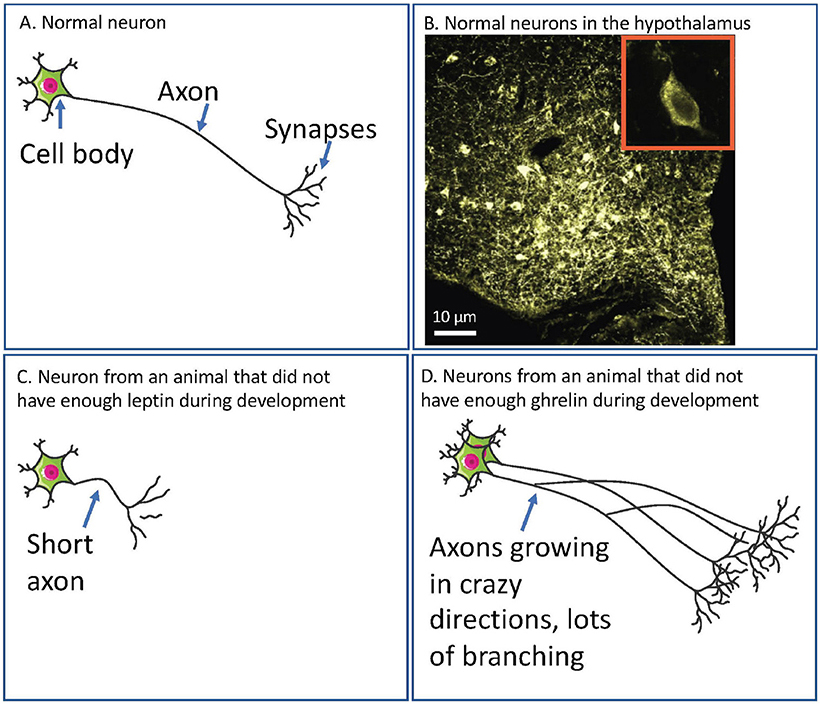
- Effigy i - (A) A diagram of a normal neuron.
- The prison cell body receives data from the external world (such equally from calorie-free if it is a neuron in your eye) or from other neurons. The axon carries the information from the cell body to the synapses. It is then passed on to other neurons or to organs of the body, like the stomach, at the synapses. (B) A microscope prototype of neurons in the hypothalamus of a rat. The big paradigm shows lots of cell bodies in yellow (the roundish blobs). The speckly coloring is the axons. Each cell body is about ten µm in diameter (i mm divided into 100 pieces). The small inset shows a zoomed in view of one cell body. The darker oval in the eye is the nucleus, which contains all the information the neuron uses to communicate. (C) If neurons in the hypothalamus do not have enough leptin, so their axons do not grow properly. This ways these axons cannot properly carry data well-nigh how full or hungry the body is. (D) If neurons in the hypothalamus do not accept enough ghrelin, and then they do non stop growing when they should. This means these axons might acquit and so many signals that the message is confused and the brain however cannot communicate effectively about how full or hungry the torso is.
In babies that have non been born even so, the neurons that ship information nearly nutrient and hunger (let us phone call these "feeding neurons") take non got the really long axons however, so they cannot talk very well to other bits of the brain. Leptin helps these axons grow. Ghrelin stops them from growing too much. If babies exercise not have enough leptin at this time, these feeding neurons cannot grow and and then tin never carry information about how hungry or full the trunk feels. If there is not enough ghrelin, these feeding neurons grow likewise much (come across Figure 1 for how this might look in the brain). In both cases, the baby can abound up unable to tell properly if it is hungry or total. The usual upshot of this for the kid growing upwardly is that he or she eats too much.
What Mom Eats Tin can Change How the Babe's Brain Develops
Scientists now know that what mom eats during pregnancy, and whether she is obese, may modify the corporeality of leptin and ghrelin in the baby. The levels of leptin and ghrelin may change the way the baby's feeding neurons grow and how the baby senses hunger when it grows up. Scientists in the by have suggested that this event is permanent. They constitute that in one case babies are by the right fourth dimension for the hypothalamus to develop at that place is nothing that tin can be done to become these feeding neurons to grow properly [four]. Just…these experiments were done in animals that could non make leptin at all. We were interested to know if these changes to the way the neurons grow could actually be reversed in normal individuals, by a balanced diet starting after the baby is born.
Using Rats and Mice to Effigy Out What is Going On in the Homo Encephalon
For most scientific studies, it is pretty hard to look inside a human brain to detect out what is going on. So, we employ what are called animal models, ordinarily rats and mice. Rats may seem very dissimilar from humans, just they are actually quite like. Rats see and smell and walk and sleep, they get tired and scared. They also get hungry, eat, and feel total. The way rats know they are hungry is because of ghrelin and leptin talking to the aforementioned part of the brain equally they do in humans, the hypothalamus.
There is one key difference between humans and rats, though. In humans, the feeding neurons commencement growing before the baby is built-in. In rats, these feeding neurons start growing after birth. In our laboratory, we can use this central difference to examination how nutrition affects ghrelin, leptin, and feeding neuron growth without affecting the mom'southward pregnancy or any other factors.
In our experiment, we took 2 groups of mother rats that had only given birth and we changed the number of babies each mother had to feed. Rat mothers usually give birth to effectually 12 babies (enquire your mom how she would like to take 12 kids all at one time!). So, feeding 12 babies is normal for a rat mother. Because it is the normal country, having 12 babies to feed is chosen a command group. Nosotros compared babies fed in lots of 12 (our control group) with babies fed in lots of only 4. When at that place are only four rat babies, they do not have to fight for their food, then they become to swallow ALL the time. Because of this they become very fat. Afterwards 3 weeks of constant eating, the babies fed in lots of 4 weighed nearly one-third more than the control group babies. That is 1 big rat!
What Happens to Leptin and Ghrelin When Babies Swallow Besides Much?
Because these fat rats drank so much more than milk and had so much more fat, they had heaps of leptin. Xiv times every bit much leptin compared with rats in the control group! Imagine if yous normally need simply one cup of milk per twenty-four hours to keep salubrious. The amount of milk the rats in our experiment drank would be like you having virtually 2 L of milk instead! These fatty rats also had much less ghrelin—probably because their bodies were trying to tell them they were not hungry.
What Happens to the Hypothalamus When Babies Eat Too Much?
Probably considering of all this actress leptin, these fat rats had much more feeding neuron growth in the hypothalamus. Even though at that place were more than feeding neurons in the hypothalamus, these feeding neurons did not work every bit hard. If we gave the fat rats leptin, the leptin failed to talk to the feeding neurons, significant that the leptin was less able to tell the brain "enough nutrient, end eating," and then the rat would eat more. Information technology is non surprising, and then, that these fatty rats cannot properly tell when they are hungry or total, and that they stay fatty as they abound up. Or is it…?
Poor Diet in Babies Tin Harm the Hypothalamus, But this Tin can Recover every bit they Grow Up
When the rats were washed feeding from their mothers' milk and it was time for them to eat solid nutrient, we gave all the rats, the fat ones and the thin ones, a healthy rat food. This food is a wee fleck dull…it looks a fleck like cardboard, and we are sure they would prefer a burger at present and so, just it is very healthy for the rats and contains all the ingredients they demand.
After these rats had all been fed this healthy nutrition for a really long time—until they were grown up, we looked at their brains. Here, nosotros found something really exciting. The feeding neurons had go normal! The feeding neurons were the same in the hypothalamus of the fat rats as they were in the control group! The grown-up fatty rats were also able to reply to leptin in the same manner that the thin, control rats did. The other actually interesting thing we found is that the hypothalamus of female person rats comes back to normal much more easily than the hypothalamus of male rats [5]. We do not know why this is, yet.
It is still not 100% good news for rats that had a poor diet when their brains were still developing. We also saw that the fat rats were sicker when they got an infection. The fatty rats were also non as good at some memory tests. And, they stay fat even on the healthy diet. But the practiced news is that, even though poor diet during evolution can mess upwards the way feeding neurons grow in the hypothalamus, the encephalon can recover from this! Our findings are exciting and encouraging for kids and adults who have health problems due to eating a poor diet in the by. Our piece of work suggests that switching to a salubrious nutrition can reverse some of the brain impairment caused past a poor nutrition.
Glossary
Hormone ("Hor-Moan"): ↑ A substance coming from one of the organs in the body that travels to another organ and tells it what to practice.
Ghrelin ("Gre-Lin"): ↑ A hormone that tells the brain to swallow more than.
Hypothalamus ("Hie-Po-Thal-A-Mus"): ↑ A brain region that is responsible for controlling feeding (and another important things).
Leptin ("Lep-Tin"): ↑ A hormone that tells the brain to stop eating.
Neuron ("New-Ron"): ↑ A cell in the brain that receives information from the body or other neurons and passes the data on. Lots of neurons together control how we respond to the information and what we think or feel about it.
Conflict of Interest Argument
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absenteeism of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed every bit a potential conflict of involvement.
Original Source Commodity
↑ Sominsky, L., Ziko, I., Nguyen, T. X., Quach, J., and Spencer, S. J. 2017. Hypothalamic effects of neonatal diet: Reversible and just partially leptin dependent. J. Endocrinol. 234:41–56. doi: 10.1530/JOE-xvi-0631
References
[1] ↑ Saper, C. B., Lowell, B. B. 2014. The hypothalamus. Curr. Biol. 24:R1111-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.ten.023
[2] ↑ Steculorum, S. Thou., Collden, G., Coupe, B., Croizier, S., Lockie, S., Andrews, Z. B., et al. 2015. Neonatal ghrelin programs development of hypothalamic feeding circuits. J. Clin. Invest. 125:846–58. doi: 10.1172/JCI73688
[3] ↑ Bouret, S. M., Draper, S. J., Simerly, R. B. 2004. Formation of projection pathways from the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus to hypothalamic regions implicated in the neural control of feeding behavior in mice. J. Neurosci. 24:2797–805. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5369-03.2004
[iv] ↑ Bouret, Southward. Yard., Draper, S. J., Simerly, R. B. 2004. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 304:108–x. doi: 10.1126/scientific discipline.1095004
[v] ↑ Ziko, I., Sominsky, 50., Nguyen, T.-X., Yam, K.-Y., De Luca, South., Korosi, A., et al. 2017. Hyperleptinemia in neonatally overfed female rats does not dysregulate feeding circuitry. Forepart. Endocrinol. 8:287. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00287
broussardconevenibary.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/401700
0 Response to "Does the Baby Start Feeding Off Your Fst if You Dont Eat Enough"
Post a Comment